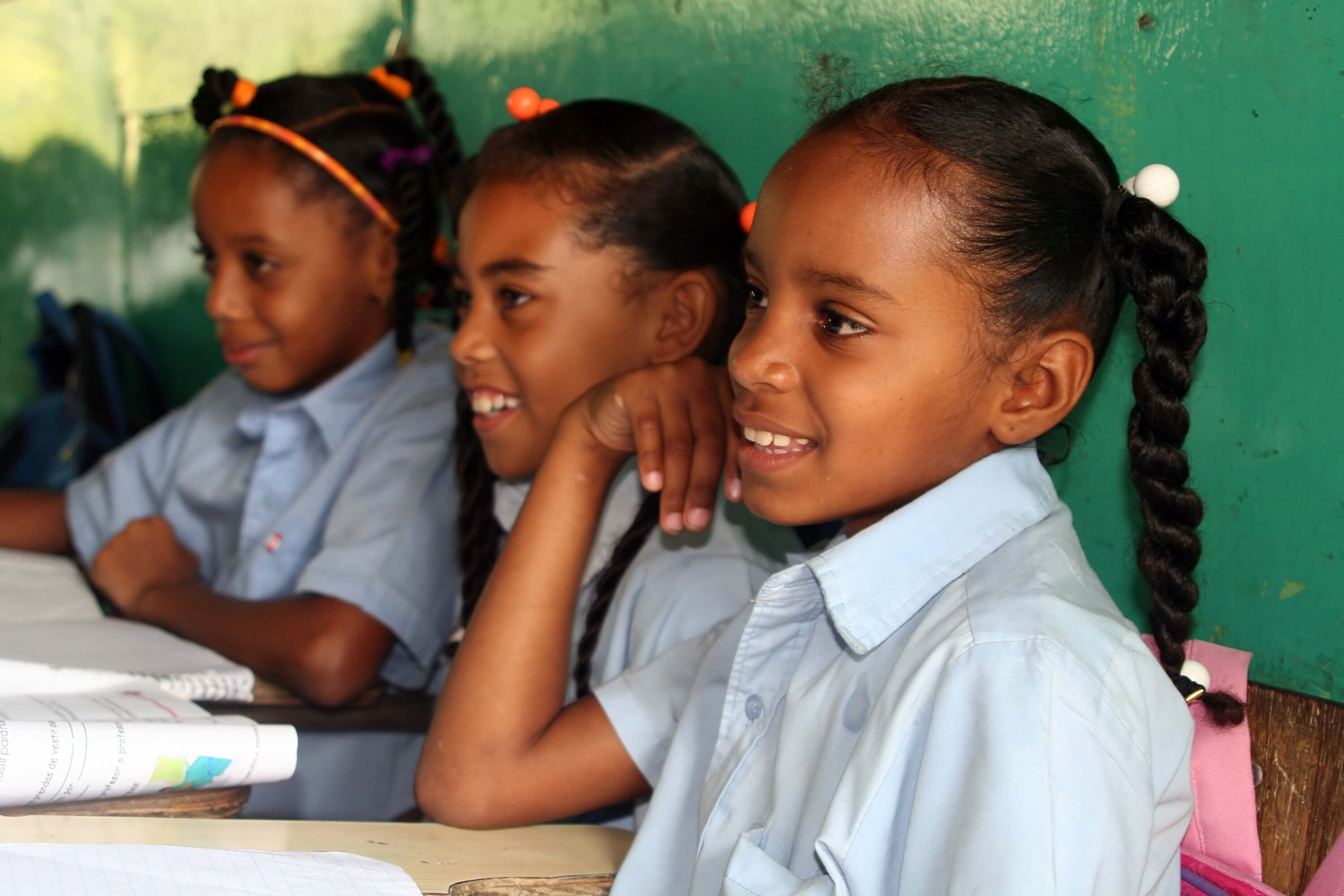
Seven Factors that Make Inclusion a Winning Strategy for Business

Inclusion and environmental sustainability are fundamental pillars for developing and managing business projects. The intersection of these concepts seeks to create more equitable environments and ensure that projects have a positive and lasting impact on communities.
IDB Invest Sustainability Week 2024. Register NOW!
Businesses, the economy, and the world win when inclusion and sustainability policies intertwine with project management, and there is an emphasis on stakeholder participation and a focus on vulnerable communities.
To promote this inclusion, we have identified the reasons that make it a winning strategy:
Project Impact on Communities: Inclusion in project management is intrinsically linked to the social and environmental impact it generates. It is essential to ensure the participation of stakeholders and the communities involved in order to foster positive outcomes. Especially susceptible groups like those in rural areas, indigenous communities, or local communities in poverty. Involving these communities from the outset helps mitigate negative impacts and generate significant benefits for all involved parties.
Sustainability Policies: A robust sustainability policy is crucial to ensure that projects are viable in the short term and contribute to the long-term well-being of communities. The policy includes plans for significant stakeholder engagement when a project may affect a community. These policies must be inclusive and consider environmental impacts as well as social and gender risks.
Focus on Gender and Diversity: Including a gender perspective in projects is another fundamental aspect of driving inclusion. Understanding that environmental and social risks can affect different groups of people differently is crucial. This is why there have been efforts to ensure that women and diverse groups are involved in community participation processes and that their specific needs, risks, and opportunities are considered. This approach is not limited to gender but also encompasses diversity in ethnicity, disabilities, and sexual orientation.
Diversity as an Inclusion Driver: Diversity should be integral to an organization's sustainability policy. Women, along with other vulnerable populations such as Afro-descendants, indigenous peoples, people with disabilities, and LGBTQI+, constitute a significant portion of the population. These populations often face additional intersecting barriers and vulnerabilities, making an inclusive approach even more crucial. Addressing these barriers promotes social justice and fosters a more inclusive and sustainable economy.
Inclusion in Rural Economy and SMEs: Inclusion should not be limited to large urban projects but extend to rural economies and small and medium-sized enterprises (SMEs). SMEs represent a significant part of the economic fabric in many regions and are often essential for providing products and services in rural areas. Ensuring these businesses have access to financing and participate in value chains is critical for effective economic inclusion.
Inclusive Economic Transformations: Transformations towards a low-carbon and digital economy must be viewed through an inclusive lens. People are at the center of these transformations, and any economic change must consider its impact on all communities, especially the most vulnerable. Just transition and inclusive economies are vital concepts that ensure no one is left behind in the development process.
- Profitability: In addition to social and environmental benefits, the positive effect on business objectives adds to the arguments for inclusion. A diverse team is better able to execute due to the diversity of perspectives and a better understanding of the market. Furthermore, products and services designed with an inclusive perspective can better serve the needs of a wider audience, thus generating higher revenue. Investing in diversity and sustainability is both ethical and profitable.
Related Content
- We Are Half the Population But Less Than One-third of Top Corporate Leaders. What Can Companies Do?
- LGBTQ+ Inclusion in the Workplace: A Business Imperative for Latin American and the Caribbean
Integrating inclusion and sustainability into project management and business models is a moral necessity and an essential strategy for long-term development. By ensuring the participation of all stakeholders and considering differentiated impacts on diverse populations, projects can generate significant benefits for both communities and businesses. Inclusion and environmental sustainability are interdependent pillars that, when implemented together, have the potential to transform our economies and societies positively.
IDB Invest Sustainability Week 2024. Click the image below to register:
LIKE WHAT YOU JUST READ?
Subscribe to our mailing list to stay informed on the latest IDB Invest news, blog posts, upcoming events, and to learn more about specific areas of interest.
Subscribe