How Can Debt Capital Markets Help Companies Survive the COVID-19 Crisis?

At the start of 2020, yearly growth for Latin America and the Caribbean countries was expected to fluctuate around 1.6 percent. Now in a global pandemic, these numbers have been adjusted to a range of -2.1 percent and -4.8 percent, according to the 2020 Latin America and Caribbean Macroeconomic Report published by the IDBG. The crisis will not only have tremendous human costs, but it will also inflict large economic costs to the region.
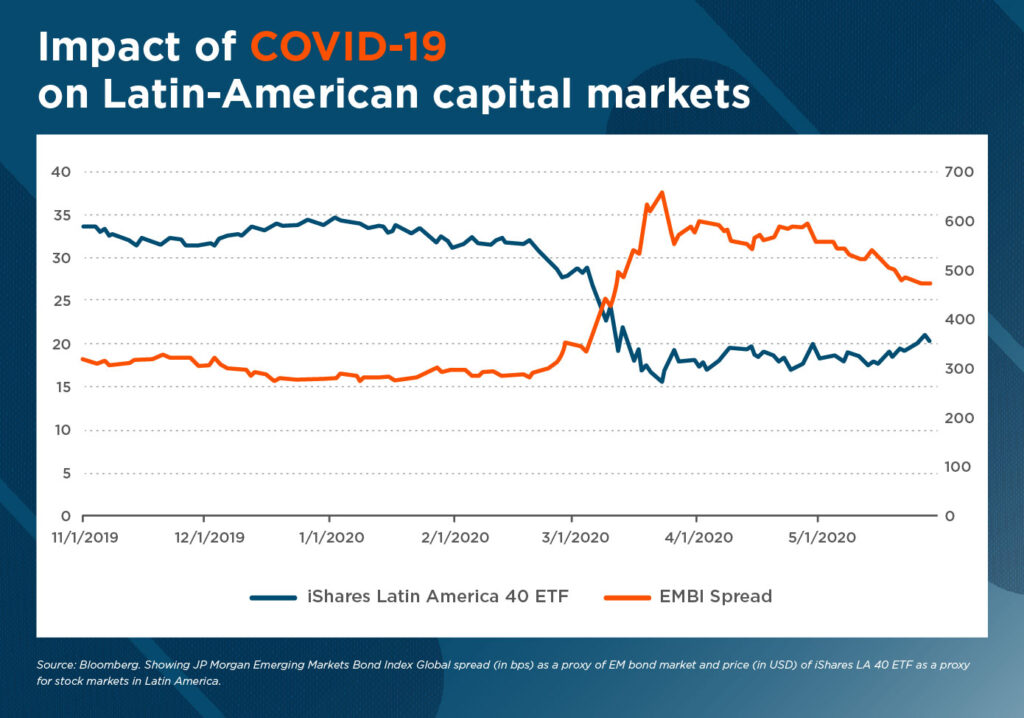
In this context, corporate bond market demand from international investors tends to shrink, which can lead to a temporary lull period. While during the past few years low interest rates scenarios in the U.S. and Europe encouraged savers to allocate part of their holdings into higher yielding quality assets in Latin America and the Caribbean, some of these inflows appear to be decreasing amid short-term macroeconomic uncertainty.
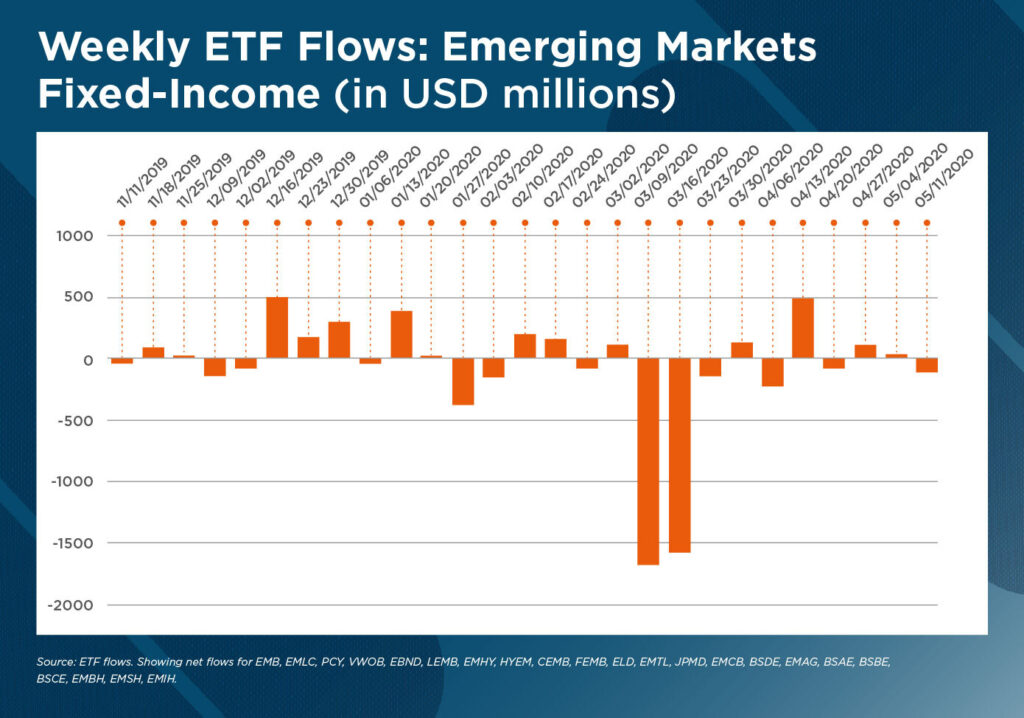
Money outflows from high yield securities are putting even more pressure on the region’s private borrowers, especially for U.S. dollars denominated debt, as credit spreads continue to spike. EMBI spreads, in fact, more than doubled from 280 basis points in December 2019 to roughly 630 at their highest point in March 2020.
Thus, the number of new debt capital markets issuances in Latin America and the Caribbean started to decrease, with high-yield corporate bond issuances, for example, down to $3.9 billion in Q1 2020, from US$5.2 billion a year before.
Bond markets as a source of liquidity
But in what way can local debt capital markets become part of the solution to the financing access puzzle in times of a global pandemic? Undoubtedly, their development in Latin America and the Caribbean economies in the early 2000s, helped mitigate the spread of the 2008 subprime mortgage crisis. Now, more than a decade later and with vast regulatory reforms undertaken at country levels, bond markets are even more prepared to act as a catalyzer for the private sector recovery.
Capital markets of the region will therefore play a decisive role: allowing companies to diversify their sources of financing away from traditional commercial lending. These firms are going to benefit from local or foreign currency bond markets that promote the efficient pricing of their debt, as well as from the access to longer tenors that match vital investments post COVID-19.
Moreover, this time the outflows from international investors are being counteracted by quick actions from regional central banks. Interest rate cuts in Peru, Brazil, Mexico, Chile and Colombia have seen positive responses from local market participants. At the same time, several monetary authorities have started implementing quantitative easing and providing emergency temporary credit lines to the most exposed citizens and business sectors.
Multilaterals and support for capital markets
It remains crucial that local and global investors regain confidence in the region’s private sector and allow it to become part of the solution for the incoming economic downturn. The role of multilateral development banks is key on providing necessary investment to debt capital markets, maintaining the access of private companies to financing through bonds, and ultimately minimizing a potential liquidity shortage by attracting and mobilizing other investors.
IDB Invest is increasing financing to protect and alleviate sectors in need of liquidity, short-term financing and working capital in times of crisis. These emergency measures are coupled with programs for longer-term financing that provide financial stability and reignite growth. In April 2020, IDB Invest increased its financing capacity from $5 billion to $7 billion for companies in the region impacted by the coronavirus pandemic.
We are committed to support debt capital raising solutions to finance initiatives with a sustainable and positive development impact. In this time of crisis, IDB Invest is doubling down. The bank provides immediate financial support to private businesses and helps them mitigate COVID-19 related social issues to bring positive and sustainable social outcomes.
To help the most vulnerable individuals and companies of the region facing a temporary shortfall of financing access, IDB Invest structures and invests in securitized notes and loans, enabling such targeted populations to improve their access to credit when they most need it. IDB Invest is structuring securities backed up by instruments such as residential mortgages, loans to SMEs and education loans. This is the case for Edilar S.A., who selected IDB Invest as a partner to structure and provide a warehouse line and securitization framework to finance quality education in Mexico. Through the process of loan aggregation, Edilar will be able to raise financing for the first time in the Mexican debt capital markets.
In addition, IDB Invest can provide a strong signal to the market on targeted issuances either via Partial Credit Guarantees, which enhance bonds credit profiles, or via anchor investments in debt securities that help attract other investors, building the confidence that the market requires in these times.■
LIKE WHAT YOU JUST READ?
Subscribe to our mailing list to stay informed on the latest IDB Invest news, blog posts, upcoming events, and to learn more about specific areas of interest.
Subscribe