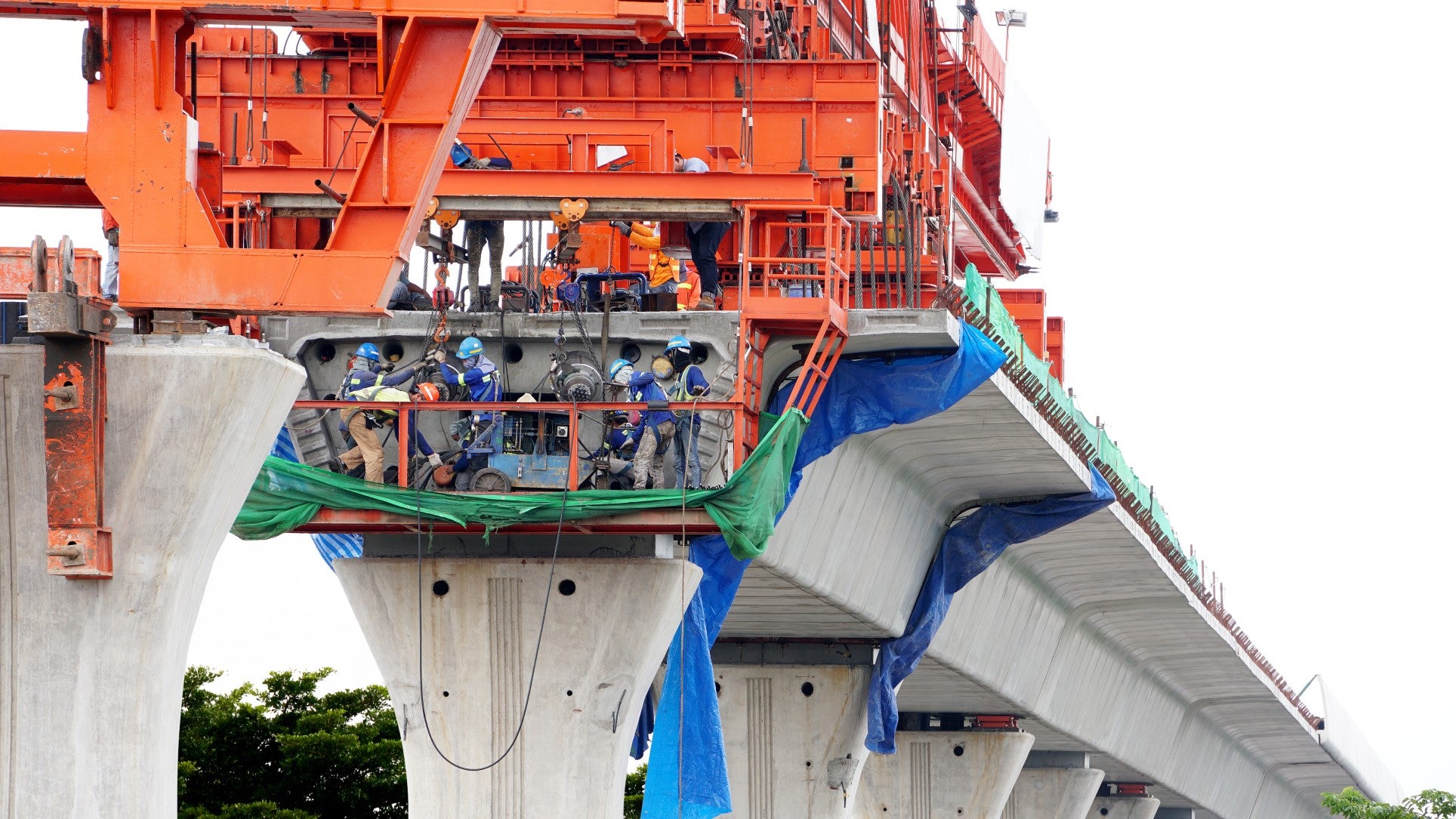
Latin-America and the Caribbean are surfing the ride-hailing wave

Thanks to smartphones, apps and new business models, the commuting experience has vastly evolved in less than a decade. Not only can we summon a car (or unlock a bicycle or e-scooter) from our smartphones, but we can enjoy perks such as a bottle of water and even candy, and then get off without even touching money or a credit card. Beforehand we also know the route, cost, arrival time and driver’s rating.
Digital technologies and business models are also enabling new mobility ecosystems. Often, these include shared solutions, upending the ownership paradigm. Cars are expensive assets which, on average, are only used 10% of their available time. Thus, technology is allowing citizens to adopt more reliable and environmentally-friendly commuting experiences. This is no mean feat considering that in-city travel is commonly cited as a painful everyday experience.
This improvement in customer welfare is creating massive amounts of wealth for the most innovative players. Uber is now valued at US$120 billion, while the ride-hailing industry boasts over 500 million users and US$60 billion in revenues. Goldman Sachs projects the industry will grow to US$285 billion by 2030, five times the size of the taxi market. And smart money follows smart ideas: sophisticated strategic investors such as Softbank, Tencent, Alphabet and Rakuten stand behind key industry players.
The popular “network effect”, prevalent among digital platforms, makes this transformational growth possible. As more riders join a ride-hailing app, more drivers are interested in attending such demand. In turn, this lowers pick-up times, creating a virtuous circle in which new riders join the platform. Interestingly, the trust in such platforms can also pave the ground for other ancillary services.
Improving the commuting experience in LAC
So, where does our region stand? As the most urbanized region in the world, Latin-American and the Caribbean’s urban dwellers suffer heavy traffic congestion, an often-collapsing road infrastructure and sometimes considerable insecurity. However, at 62% of total mobile connections, smartphone penetration is adequate and increasing rapidly. This has allowed 36 million people to adopt ride-hailing, making trips through companies like Uber, Cabify, Easy Taxi, 99, Beat, Taxify, Nekso, among others.
Global investors are sourcing capital, with Chinese behemoth Didi Chuxing taking control of 99 and allowing the company to expand from Brazil to Mexico. Competition and partnerships will intensify both vertically and horizontally, roping in car makers that are developing both autonomous and electric vehicles, bike sharing, food delivery business models, fintech providers and others.
As in any disruption process, there are challenges and difficult questions with no definitive answers. Technology evolves fast and, naturally, regulators struggle to keep pace. Different countries have dissimilar approaches towards the rapidly growing gig economy. Each city, in turn, shows its own nuances, and the effect on its public transport systems is thus unique. Finally, there are those who feel threatened by the changes introduced with these technology-enabled business models.
We are of the view that when a service efficiently addresses a concrete need, it is here to stay. And such is the case of ride-hailing. Rather than remaining a spectator, IDB Invest has taken an active approach. We are supporting the enabling environment through numerous financings for mobile broadband networks and smartphones. But we also wanted to play a role in forging best practices in the ride-hailing industry itself. In December, together with Blue Like an Orange Capital, we structured a US$70 million mezzanine financing to Maxi Mobility. The group is backed by conciliatory and development-minded sponsors, who operate the Cabify and Easy Taxi brands across LAC. A portion of the proceeds will be applied to rolling out a fintech platform, which will further contribute to financial inclusion of drivers and riders.
Next time you need a ride, just tap your smartphone and you’ll be on your way by car, motorcycle or e-scooter. And remember to use the right provider: one that is environmentally minded and that acts with integrity towards all stakeholders.
LEARN HOW IDB INVEST CAN OFFER YOU SOLUTIONS HERE.
LIKE WHAT YOU JUST READ?
Subscribe to our mailing list to stay informed on the latest IDB Invest news, blog posts, upcoming events, and to learn more about specific areas of interest.
Subscribe